- issued by Basel Committee on Banking Supervision (BCBS)
- Basel (Switzerland) is HQ for Bureau of International Settlements (BIS)
- BIS promotes cooperation among central banks w/ common goal of financial stability and banking regulatory standards
- Basel Accords: set of agreements by BCBS primarily addressing risks associated w/ banks & financial system
- accepted by India
- in fact, RBI has more stringent standards on few parameters than BCBS
Goal of Basel Norms
Ensuring that FI have sufficient capital to meet obligations and absorb expected losses.
Basel I
- introduced capital mgmt system Basel Capital Accord 1988
- India adopted it in 1991
- entirely concerned with credit risk
- no concern for market & operational risk
- estd. capital and risk weighed structure for bank in form of Capital Adequacy Ratio (CAR 🚗)
What are Risk Weighted Assets?
- weighing bank’s assets (i.e. loans) in context of the associated risk
- eg. credit card loans most risky as they have no security other than promise
- secured loans safer as collateral can be used to recover loan amount even if borrower does not pay back
- more risk taken by bank more capital needed to protect depositors
- required minimum capital 8% of RWA
- but RBI enforces 9%
Types of Capital
Tier I
- bank’s core capital
- primary measure of bank’s financial strength
- very liquid, can be used w/o shutting down operations
- incl. retained earnings
- majority of core capital is made of disclosed reserves, equity
- most of the equity portion will be common equity which will have no conditions attached
Tier II
- used for supplemental funding since less reliable
- incl. undisclosed reserves (from bank owners), preferential shares, subordinate debt
Basel II
- June 2004
- considered to be refined and reformed version of Basel I
Guidelines were formed on 3 pillars:
- Capital Adequacy Requirements
- same at 8%, but now considered all 3 risks:
- credit
- market
- operational
- same at 8%, but now considered all 3 risks:
- Supervisory Review
- banks required to develop & implement better risk mgmt techniques for monitoring & managing all 3 types of risks
- Market Discipline
- requires strict disclosure requirements
- banks must report their CAR, Risk exposure, other info to central bank on regular basis
After 2008 financial crisis & collapse of Lehmann Brothers Bank, the need for better guidelines was seen.
Basel III
- in the wake of Lehmann Brothers collapse & financial crisis, BCBS decided to strengthen norms
- new guidelines intended to promote more resilient banking system, by focusing on 4 critical banking parameters
- capital
- leverage
- funding
- liquidity
- focus on better capital quality, which came from higher loss absorbing capacity
- also suggested addl. capital conservation buffers and counter cyclical buffers
Capital Conservation Buffer
- banks must hold capital conservation buffer of 2.5%
- focus of this buffer to ensure banks maintain a cushion of capital that can be used to absorb losses during periods of financial & economic stress
Countercyclical Buffer
- introduced w/ objective of:
- increasing capital requirements during good times
- decreasing during crisis
- buffer will slow down banking activities when economy overheats and it’ll encourage lending during crisis
- buffer will range from 0-2.5% & will consist of common equity or other loss absorbing capital
- it’s buffer of capital maintained by banks in good times, which may be used to maintain credit flow in difficult times
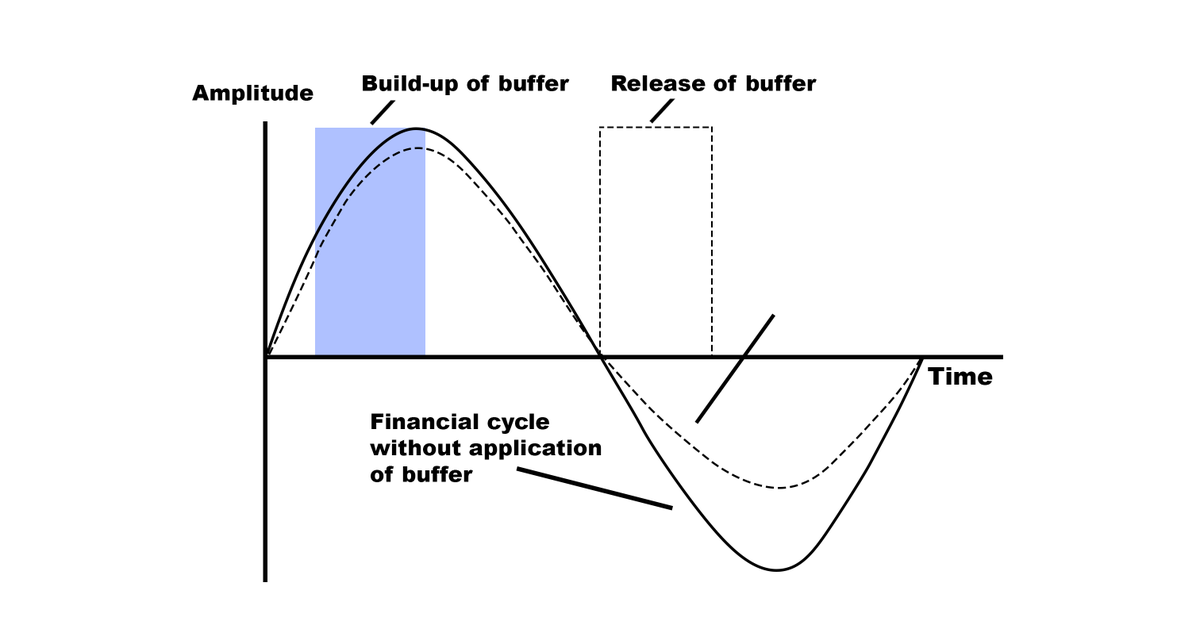
- will discourage banks from giving too many loans during good economic conditions
- some of them may become NPA when economic conditions weak
- maintaining CCB will also reduce lending ability of bank
- banks bust set aside CCB so that banks remain adequately capitalized when loans extended by banks start turning into bad loans